Sex Education - Male Reproductive System | पुरुष प्रजनन तंत्र
What is Reproduction?
Reproduction is the biological process of producing its own offspring of the same kind. It is one of the essential processes that help in providing the continuation of the species, generation after generations.
There are two different types of reproduction:
- Sexual reproduction.
- Asexual reproduction.
Let’s have a look at the male reproductive system that represents different parts or organs of the male reproductive system.
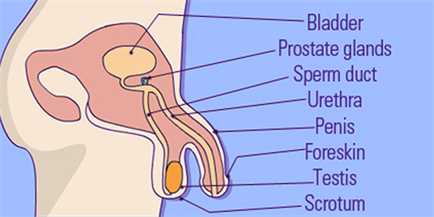
Male reproductive system
The male reproductive system includes testes, scrotum, spermatic ducts, sex glands, and penis. All these organs work together to produce sperms, male gamete, and other components of semen.
- Penis and Urethra are a part of reproductive and urinary systems.
- Scrotum, seminal vesicles, vas deferens, testicles (testes), and prostate constitute all the remaining reproductive system.
The Penis has a root that is connected to the structures of both the pelvic bones and lower abdominal (the shaft’s visible part) glands that has a cone-shaped end. Urethra’s opening is the channel that carries semen and urine and lies at the tip of the penis. The base of the penis is known as Corona.
Penis
It involves three cylindrical spaces of erectile tissue. The two which are larger, the corpora cavernosa lie side by side and the third one is sinus, called corpus spongiosum covers the urethra. The penis becomes rigid when these spaces are filled by the blood.
Scrotum
It is a sac of thick skin that protects and surrounds the testes. It also controls the temperature of the testes since they have to be at a slightly lower temperature than the body temperature for suitable sperm creation. The muscles in the wall allow the testes to hang far from the body or shrink to pull them closer for protection and warmth.
Testes
They are the oval bodies, around 1.5 to 3 inches in length. Generally, the left testis hangs slightly lower than the right one.
The two primary functions of tests are as follows:
- Producing testosterone – a male sex hormone.
- Producing sperms -a carrier of man’s genes.
The Seminal vesicles are present over the prostate, linked with the vas deferens to create the ejaculatory ducts that travel through the prostate. The seminal vesicles and prostate generate fluid which nourishes the sperm. This fluid provides a maximum volume of the semen, wherein the sperm is ejected during ejaculation.
Urethra
It is a tube-like structure that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus. In males, the urethra travels through the penis and is mainly involved in two main functions:
- This region is included in the urinary tract that takes urine from the bladder where semen is ejaculated.
- The Prostate exists beneath the bladder and covers the urethra. The prostate grows larger with age. If the prostate grows too much, it can block the urine flow through the urethra and be responsible for some urinary symptoms.











































0 Comments: