Asexual Reproduction Definition
“Asexual reproduction is the mode of reproduction that is involved in the production of offsprings by a single parent.”
What is Asexual Reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction in which a new offspring is produced by a single parent. The new individuals produced are genetically and physically identical to each other, i.e., they are the clones of their parent.
Asexual reproduction is observed in both multicellular and unicellular organisms. This process does not involve any kind of gamete fusion and there won’t be any change in the number of chromosomes either. It will inherit the same genes as the parent, except for some cases where there is a chance of rare mutation to occur.
Also Read: Reproduction
Characteristics of Asexual Reproduction
Following are the important features of asexual reproduction:
- Single parent involved.
- No fertilization or gamete formation takes place.
- This process of reproduction occurs in a very short time.
- The organisms multiply and grow rapidly.
- The offspring is genetically similar.
Types of Asexual Reproduction
There are different types of asexual reproduction:
- Binary Fission
- Budding
- Fragmentation
- Vegetative Propagation
- Sporogenesis
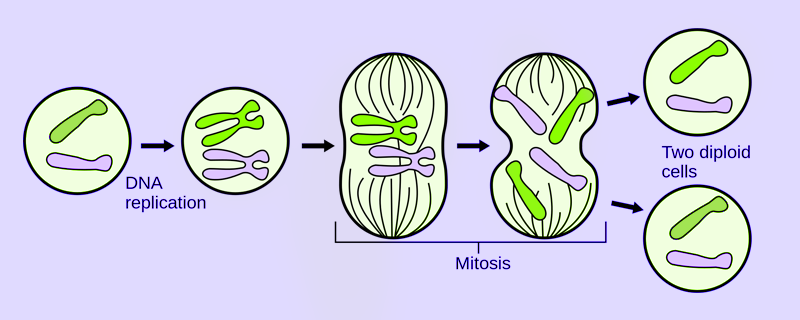
Binary Fission
The term “fission” means “to divide”. During binary fission, the parent cell divides into two cells. The cell division patterns vary in different organisms, i.e., some are directional while others are non-directional. Amoeba and euglena exhibit binary fission.
It is one of the simplest and uncomplicated methods of asexual reproduction. The parent cell divides into two, each daughter cell carrying a nucleus of its own that is genetically identical to the parent. The cytoplasm also divides leading to two equal-sized daughter cells. The process repeats itself and the daughter cells grow and further divide.
Fragmentation
Fragmentation is another mode of asexual reproduction exhibited by organisms such as spirogyra, planaria etc. The parent body divides into several fragments and each fragment develops into a new organism.
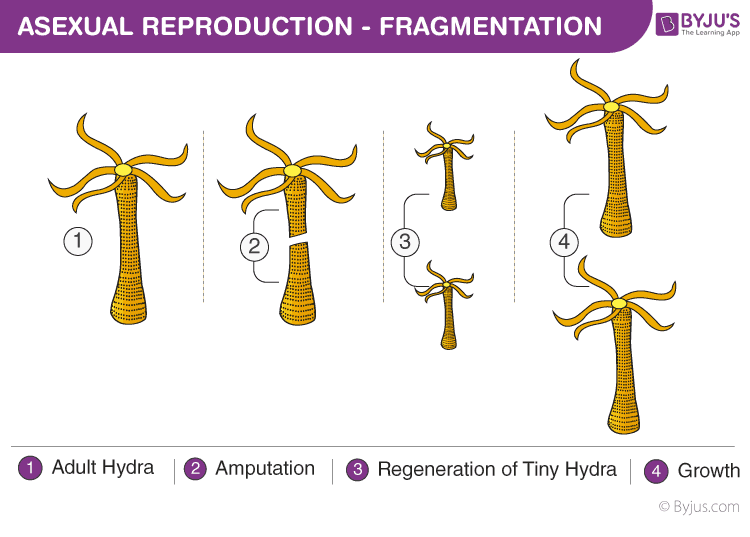
Also Read: Fragmentation
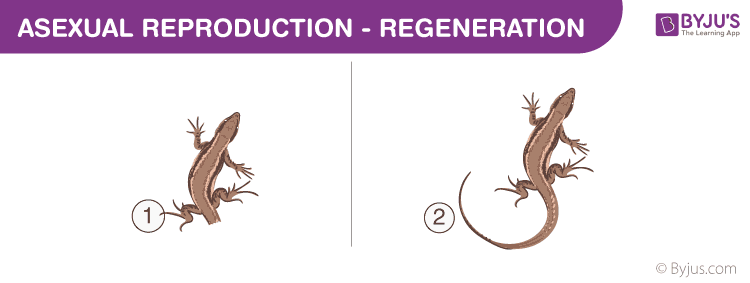
Regeneration
Regeneration is the power of growing a new organism from the lost body part. For eg., when a lizard loses its tail, a new tail grows. This is because the specialized cells present in the organism can differentiate and grow into a new individual. Organisms like hydra and planaria exhibit regeneration.
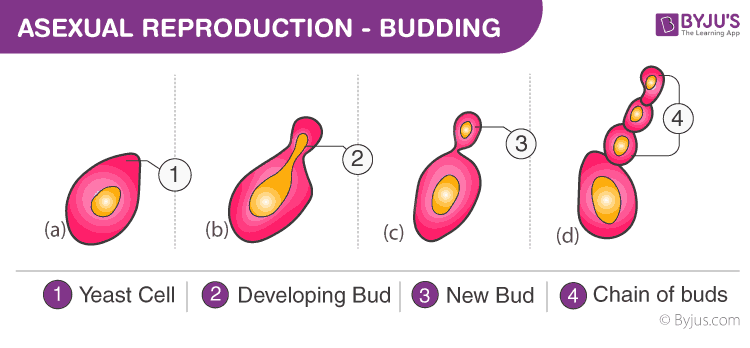
Budding
Budding is the process of producing an individual through the buds that develop on the parent body. Hydra is an organism that reproduces by budding. The bud derives nutrition and shelter from the parent organism and detaches once it is fully grown.
Vegetative Propagation
Asexual reproduction in plants occurs through their vegetative parts such as leaves, roots, stem, and buds. This is called vegetative propagation. For example, potato tubers, runners/stolon, onion bulbs, etc., all reproduce through vegetative propagation.
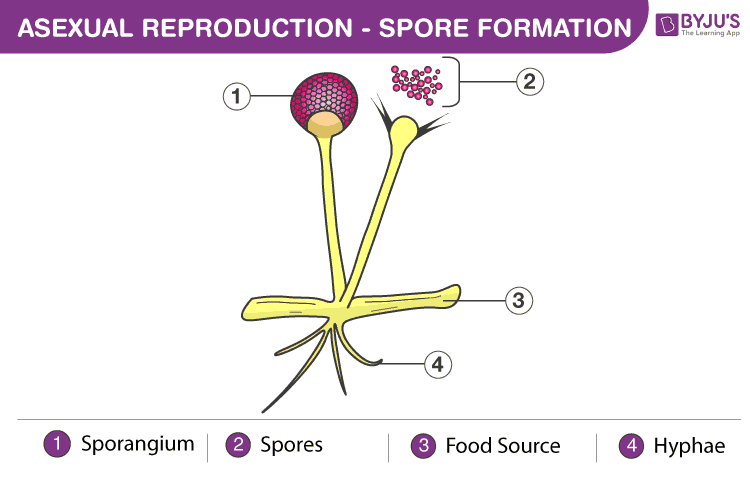
Spore Formation
Spore formation is another means of asexual reproduction. During unfavourable conditions, the organism develops sac-like structures called sporangium that contain spores. When the conditions are favourable, the sporangium burst opens and spores are released that germinate to give rise to new organisms.
In asexual reproduction, a single cell is divided to produce offspring. The simple cell-by-cell division is not possible in multicellular organisms. Most of the multicellular organisms have a complex body design. They have a higher level of organization like tissues, organs and organ system. Thus, they need a special mode for reproduction.
Also Read: Modes of Reproduction
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
Following are the advantages of asexual reproduction:
- Mates not required.
- The process of reproduction is rapid.
- An enormous number of organisms can be produced in very less time.
- Positive genetic influences pass on to successive generations.
- It occurs in various environments.
Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction
The major disadvantages of asexual reproduction are:
- Lack of diversity. Since the off springs are genetically identical to the parent they are more susceptible to the same diseases and nutrient deficiencies as the parent. All the negative mutations persist for generations.
- Since only one organism is involved, the diversity among the organisms is limited.
- They are unable to adapt to the changing environment.
- A single change in the environment would eliminate the entire species.
Asexual Reproduction Examples
Following are the examples of asexual reproduction:
- Bacterium undergoes binary fission in which the cell divides into two along with the nucleus.
- Blackworms or mudworms reproduce through fragmentation.
- Hydras reproduce through budding.
- Organisms such as copperheads undergo parthenogenesis.
- Sugarcane can be grown through vegetative propagation.
Also Read: Sexual Reproduction
सेक्सुअल रिप्रोडक्शन परिभाषा;
"एसेक्सुअल रिप्रोडक्शन, प्रजनन का वह तरीका है जो एकल माता-पिता द्वारा संतानों के उत्पादन में शामिल होता है।"
एसेक्सुअल रिप्रोडक्शन क्या है?
एसेक्सुअल रिप्रोडक्शन के लक्षण
एसेक्सुअल रिप्रोडक्शन के प्रकार

विखंडन

उत्थान

उबटन लगाना

वनस्पति प्रचार



0 Comments: