Sex Education - Fertilization and implantation | षेचन और आरोपण
Sex Education - Fertilization and implantation | षेचन और आरोपण |
Fertilization and implantation are the most critical events in the reproduction process. In this process, both egg and sperm are fused together to form a zygote. Later it gets implanted into the uterus and the development of an organism.
Let us have a look at how fertilization in humans takes place.
Fertilization in Humans
“Fertilization in humans refers to the fusion of male and female gametes that facilitates the development of a new organism.”
Fertilization is the natural life process, which is carried out by the fusion of both male and female gametes, which results in the formation of a zygote. In humans, the process of fertilization takes place in the fallopian tube.
During this process, semen comprising thousands of sperms are inseminated into the female vagina during coitus. The sperms move towards the uterus and reach the opening of the fallopian tube. only a few sperms will succeed in reaching the opening of the fallopian tube.
The secondary oocyte releases from the matured Grafian follicle of the ovary and enters into the fallopian tube, where it is fertilized within 24 hours, after which it is released from the ovary.
Though surrounded by several sperms, the oocyte is fertilized by a single sperm. During meiosis-II, the sperm enters the secondary oocyte and completes the meiosis. After this, the secondary oocyte is known as the egg.
Both sperm and egg can show their vitality only to a limited period. Sperm is alive for 48-72 hours in a female reproductive system, whereas the egg can be fertilized for 24 hours before it is released.
Also Read: Internal and External Fertilization
Steps of Fertilization in Humans
The fertilization process in humans takes place in several stages involving both the chemical and physical events. The different stages of fertilization in humans are mentioned below:
Acrosomal Reaction
The sperms incapacitation undergo acrosomal reactions and release certain chemicals known as sperm lysins present in the acrosome.
Due to the acrosomal reactions, the plasma membrane of the secondary oocyte and the sperm are fused together so that the contents of the sperms can enter. When the plasma membrane of the sperm binds with that of the secondary oocyte, the plasma membrane of the oocyte depolarizes. This prevents polyspermy.
Calcium ions play a significant role in the acrosomal reaction. The main factors essential for acrosomal reactions are optimum pH, temperature and calcium and magnesium concentration.
Cortical Reaction
Soon after the fusion of the plasma membranes, the oocyte shows cortical reactions. Cortical granules found under the plasma membrane of the oocyte, which fuses with the plasma membrane and releases cortical enzymes between the zona pellucida and plasma membrane. The zona pellucida is hardened by the cortical enzymes that prevent polyspermy.
Sperm Entry
A projection known as the cone of reception is formed by the secondary oocyte at the point of sperm contact. This cone of reception receives the sperm.
Karyogamy
After the entry of the sperm, the suspended second meiotic division is completed by the secondary oocyte. This gives rise to a haploid ovum and a second polar body.
The head of the sperm containing the nucleus detaches from the entire sperm and is known as male pronucleus. The tail and the second polar body degenerates. The nucleus of the ovum is known as female pronuclei.
The male and female pronuclei fuse and their nuclear membranes degenerate. The fusion of the chromosomes of male and female gametes is called karyogamy. The ovum is now fertilized and is known as a zygote.
Activation of Eggs
The entry of sperm triggers the metabolism in the zygote. Consequently, protein synthesis and cellular respiration increase.
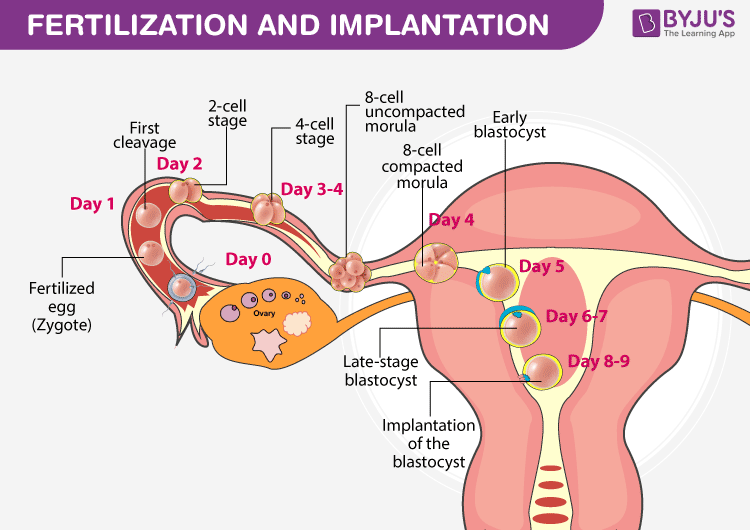
Implantation
Once fertilization happens, the cell starts to divide and multiply within 24 hours in the fallopian tube. This detached multi-celled structure is called a zygote. Later, after 3-4 days it travels to the uterus and now we call it as an embryo.
The embryo develops and undergoes various stages and gets attached to the endometrial layer of the uterus. This process of attachment is known as implantation.
Also Read: Implantation
Sex Determination
Fertilization is the process in which a new cell is formed when two gametes (sex cells) –sperm and ova fuse together. During this unbiased event, all genetic information is transferred from both the parents to their child and the gender of the child is determined.
Father determines the sex of the child, i.e. if the sperm carries a Y chromosome, the child will be a boy and if sperm carries X chromosome child will be a girl.
Also read: Determination Of Sex
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the human fertilization?
The fusion of male and female gametes occurring in the ampulla of the fallopian tube is known as fertilization in humans.
How long does it take for the egg to get fertilized?
The egg is alive for about 12-24 hours after its release from the ovary. If it is not fertilized by this time, it disintegrates and is shed off by the uterine lining.
How long does sperm live?
The sperm stays alive for about 72 hours. The sperms swim upwards to the fallopian tube to fertilize the egg. The faster the sperm swims, the earlier it reaches the egg.
What are the different phases of fertilization?
The different phases of fertilization include- penetration, where the sperm releases acrosomal enzymes to penetrate inside the egg; activation, where the egg membrane depolarizes; and fusion of nuclei and formation of zygote.
What is the sole purpose of fertilization?
The main purpose of fertilization is to combine the haploid chromosome sets of two individuals into a single diploid cell known as the zygote which is the result of activation of the egg.
What are the different types of fertilization?
There are two different types of fertilization- internal fertilization, where the fusion of egg and sperm occurs inside the female reproductive tract, for eg., humans; and external fertilization, where the fusion of male and female gametes occurs outside the body of the organism, for eg., sea urchins, frogs, etc.
What would happen if fertilization does not occur?
If fertilization does not occur, there will be no zygote formation and egg will degenerate and shed through the uterine lining.
What is implantation?
Implantation is the stage where the embryo adheres to the wall of the uterus.





















